
Identifying a need for a web design project is the first step. Collecting data to understand the user’s wants, needs, challenges, and goals is pivotal. Research should be used to generate strategic objectives and define project specifications.
Defining a target audience allows focusing on defining the look, feel, and message that will resonate with them. Pinpointing desired outcomes helps build the content plan required to succeed in meeting those aims. These components and further research should then define the website structure—the architecture of pages, navigation hierarchy, color palette, and so on.
Wireframing a visual representation of your design style—is used to map out where important elements are placed and how they fit together on each page or view. This critical step informs all subsequent decisions regarding designing and developing your website’s UI (User Interface).
Using interactive prototyping tools brings your wireframes to life. Animations, transitions, and interactions are incorporated, giving you confidence in the user experience and visual appeal. Feedback can be gathered from internal and external users through user testing scripts or surveys, helping refine concepts further where necessary for the website development team.
1. Discovery
Requirements Gathering

Recognizing the importance of understanding user needs is a prerequisite for creating successful digital solutions. Requirements gathering is the process of discovering, documenting, and analyzing those needs.
At its core, requirements gathering involves getting an eagle-eye view of expectations from multiple stakeholders. It turns otherwise nebulous visions into measurable outcomes and ensures that all perspectives are considered.
Successful requirements gathering requires a combination of effective communication and efficient synthesis. It’s essential to listen deeply and pay attention to details others may overlook; enquiring beyond binary yes-no answers dives deeper into nuanced user desires.
The organization is key in keeping track of what has been gathered through extensive note-taking or structured questionnaires – whatever suits your workflow to keep yourself on top of things. An organized overview allows inconsistencies to be easily identified before concluding the data collected.
Overall, with carefully executed requirements gathering, you will better understand user needs and build meaningful rough designs that satisfy those needs and simultaneously provide suitable functions.
2. Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a technique widely used to generate creative and innovative ideas.

How Can Brainstorming be used for Web Design Ideas?
It involves groups of people coming together to discuss and explore potential solutions without criticism about the ideas discussed. Applying this to website design inspiration can bring superior results as it helps identify target users, develop an appropriate user experience, and develop engaging designs.
For example, during a brainstorming session, one component of the web design phase that can be explored is target audiences. What are their needs and wants?
Participants can share their insights on elements like demographics, psychographics (attitudes and lifestyles), shopping behaviors, and device preferences.
With this knowledge, websites can be tailored more effectively toward the chosen audience group’s specific requirements.
Furthermore, brainstorming can inspire team members to generate unique user experiences as different groups suggest various experiential components such as website navigation flow suggestions or promotional campaigns.
Once enthusiasm has been established to target market insights and user experience ideas, a web design company can create exciting designs based on these elements discussed in the session. Understanding the importance of user experience in design is crucial for achieving a successful outcome. By prioritizing user needs and preferences, designers can create intuitive interfaces that foster engagement and satisfaction. This approach not only enhances the aesthetic appeal but also ensures functionality, leading to a more effective product.
Visuals generated may vary depending on popular trends among sure generations or industries. In contrast, specific audiences might prefer visuals with minimalistic styling to stand out from competitors in their sector without going over the top with graphics implements.
To ensure that all participants stay engaged throughout the brainstorming session, it is also important to consider techniques like role play or activities like “There’s no such thing as a bad idea,” which encourages everyone in the group to continuously throw out new ideas until they are completely confident that they have exhausted every avenue of thought on the subject under discussion.
To conclude a practical brainstorming session on web design concepts, collate all of the ideas into an action plan which outlines tasks that need completing before implementing any changes, such as drawing up site maps or mockups for concepts discussed for testing purposes before going live with any of them.
3. Web Design Project Workflow
Web Design Project Workflows are the processes and steps that must be followed to create websites or web applications.
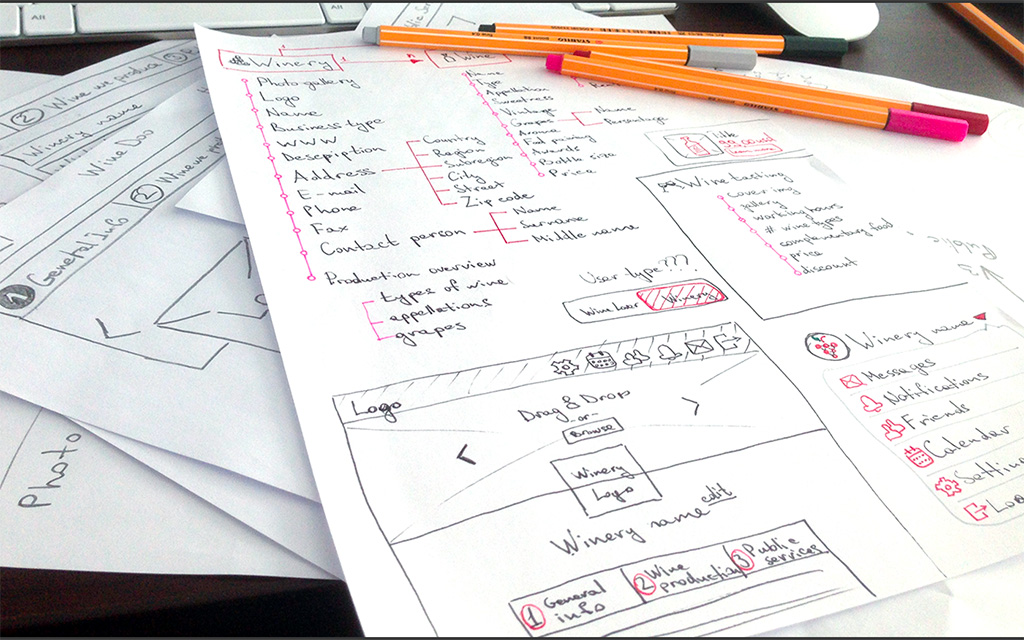
What is a Web Design Project Workflow?
The modern custom web design process workflows are the processes and steps that must be followed to create websites or web applications. A good workflow ensures an efficient, successful, and organized production from start to finish. It also helps ensure that all involved parties understand their roles, tasks, and responsibilities for each initial stage of the project.
Workflows consist of a series of interconnected visual elements, including tasks, activities, discussions, documentation, reviews, approvals, decisions, and notifications. Every step must be complemented with a timeline for projects to move forward quickly and seamlessly.
At the outset, it is essential to establish who will be responsible for specific tasks during different stages of the process and create detailed timelines of when those tasks should be completed according to client expectations.
Each step should also include any requirements, such as deliverables or feedback needed by other team members, for them to move on with their respective tasks as scheduled.
This will help avoid misunderstandings over expectations and eliminate areas where too much work is done by one person. Therefore, creating an environment of timeline efficiency. Having automated notifications like emails allows everyone involved in the project to track its progress with ease leading up to the completion of any task without necessarily having meetings or other forms of direct communication every step of the way. to maximize efficiency, schedule your discovery call today to align on objectives and deliverables. By streamlining communication from the outset, teams can ensure that timelines are adhered to and responsibilities are clear. This proactive approach fosters collaboration and reduces the likelihood of roadblocks throughout the project.
When creating a workflow for web design projects, several significant considerations must be taken into account from start to finish including:
- Research & discovery (overall goals/objectives)
- Wireframing (website structure/design layout)
- Design (visual style guide/branding)
- Coding & programming (front-end development stage)
- Integration & testing (functionality/speed optimization)
- Delivery (final product launch)
All elements need to be completed for each step to transition fluently into the following, providing clients with tangible products at regular intervals that adhere strictly to their needs and industry standards.
4. Low-fidelity Wireframes
Visual Design for Low-fidelity Wireframes is the process of creating visuals that adhere to the design standards of a web or application project.

What is Visual Design for Low-fidelity Wireframes?
This visual representation serves as a prototype for the final product and can assist in communicating ideas to stakeholders and developers. This process incorporates interface elements such as fonts, color schemes, icons, buttons, and navigation components into the wireframe to create a clear flow of information.
The goal of this endeavor is to produce an accurate representation of how users will interact with specific locations within a digital platform. It allows stakeholders to envision how users will experience applications from various perspectives by focusing on core functionalities and UI elements to provide better user guidance in creation. By creating low-fi visuals that meet current industry trends and technological capabilities, design companies can clearly show their vision for the product or service.
Low-fi wireframes help designers determine which areas require their attention before moving forward with high-fi implementations by analyzing usability flow patterns throughout applications or websites using specific tools like Adobe’s XD content prototyping suite. Additionally, it gives developers an indication of where significant problems may arise when integrating back-end services while ensuring that they remain within design guidelines.
By introducing visually appealing elements into low-fidelity wireframes through careful selection of typography and pleasing color palettes, designers strive to bring design objectives alive without disrupting functionality, allowing stakeholders and engineers alike accurately visualize what success looks like before further investments are made into the development team efforts. With continued practice and refinement over time, knowledge gained from visualizing digital projects provides invaluable insight for future endeavors to create intuitive structures for complex web applications enabling teams to be fully prepared before releasing products out into the wild.
5. High-fidelity Wireframes
Visualizing high-fidelity wireframes requires taking conceptual ideas and the core structure of the user interface and crafting it into a visual representation that will guide users through their experience.
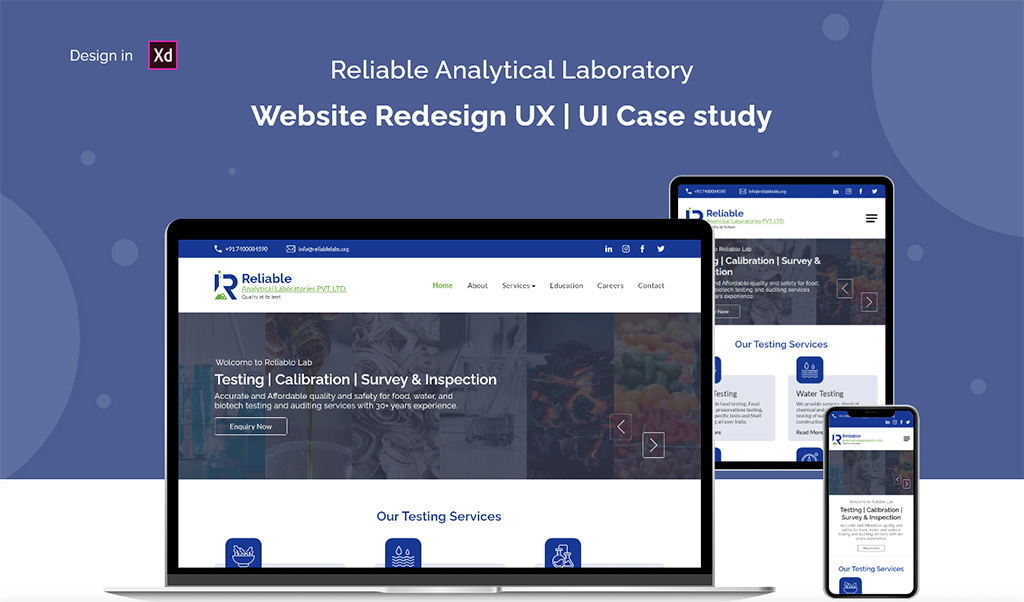
What is Involved with Creating Visual Design for High-fidelity Wireframes?
To create visually pleasing wireframes, designers must focus on how people interact with the content structure while providing clarity in design.
Designers applying visual design to a high-fidelity wireframe must pay attention to every aesthetic detail, such as typography, shapes, color scale, and font style. A well-thought-out visual design system should balance strong visuals and subtle details, offering cues for how users behave.
Assembling these correct elements helps identify which options are most accurate for representing an entity’s brand regarding colors, iconography, images, white space, textiles, and animation – from basic low-fidelity paper sketching to complete high-fidelity designs that deliver rich interactive moments. It instructs content writing streamlining by recognizing what components associate closely together to create synergy within the overall interface.
Using grid systems offers designers a greater set of guidelines when creating their wireframes, as it assists in aligning elements according to each other rather than relying on guesswork. Developers also use grids as they help them develop more cohesive UI components and better consistency among all pages. This greatly reduces testing time as they can effortlessly move back and forth between different template outputs quickly while maintaining synonymy amongst visuals layout-wise across all platforms or devices used by customers.
Furthermore, establishing relationships between frontend elements throughout the interface becomes streamlined when using effective systems like grids upfront instead of frantically trying to reconcile them after the fact at times when prototyping begins or if changes need to be made along the way due to a change in requirements.
6. Visual Mockups
Visual mockups are an essential part of the user experience design process. It’s a way to present your ideas quickly and communicate them effectively to clients, teammates, and stakeholders.
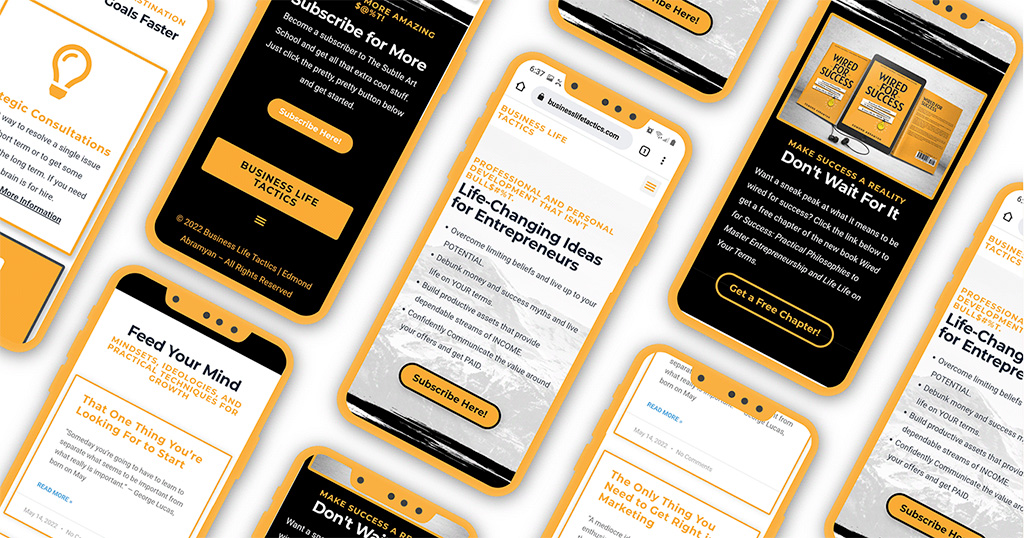
What is Visual Mockup Development?
A visual mockup helps test a product concept before over-investing in the development process or reimplementing changes after launch. It also provides a realistic representation of how the end product will look and feel, which can be invaluable when launching a new product or revising an existing one.
Mockup development projects involve building high-fidelity visuals representing key layouts and interaction behaviors for user testing or stakeholder presentations. This may include creating prototypes with interactive components such as buttons, menus, sliders, swipes, etc., all designed with precise attention to detail. Developing these visuals requires knowledge of UI/UX best practices and graphic design principles to create visually appealing yet highly functional layouts that meet user requirements and design specs.
The goal of visual mockups should consistently be achieving clarity and understanding of what needs to be built from both a user interface perspective and a technical standpoint. To ensure this happens, designers need to test their designs with users before presenting them for further consideration or feedback; this will reduce guesswork when coding the actual implementation later on. Additionally, it’s essential to ensure consistency between all visuals used by choosing the right fonts, colors, icons, and patterns while avoiding distraction through clutter or unnecessary complexity.
Once developed, visual content mockups can be an excellent starting point for building genuinely great products and also aid in avoiding scope creep.
They provide project owners with tangible representations of what’s expected at each stage and a basis for collaboration between all cross-functional design teams involved in the process. Visual mockup development technology is also relatively fast if appropriately done, as getting feedback makes it easier to iterate earlier before committing too much effort towards the development life cycle.
However, it is essential to avoid becoming too dependent on static designs. Static web designs are the building blocks of a website and are involved in creating all aspects of the website. A static design is not dynamic, meaning it does not change when visitors click on different elements or sections of the page. Although static designs have proven incredibly effective for creating attractive website layouts, there are certain disadvantages associated with relying solely on them.
7. Development Phase
The website development phase is the final stage of the web development cycle. It involves implementing the code and design elements to create a functional Content Management System.

What is the Website Development Phase?
All planned features and functions are added to the site during this phase and optimized for user experience. The website development phase also includes testing and debugging.
At this stage, developers will analyze any potential bugs or issues with the functioning of a website. This allows them to make necessary changes before launch. If done properly, this should ensure that the site runs smoothly after launch day.
During the website development phase, SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is often implemented to ensure that the website ranks well in search engine results pages (SERP).
SEO best practices involve optimizing content creation for targeted keywords, creating meta tags and descriptions for each page, optimizing for mobile users, developing internal linking between pages on their respective sites, and using external links from reputable websites in relevant topics across industries.
In addition, many organizations choose to add analytics tools during this stage to monitor usage patterns over time and track visitors’ behavior on their websites.
These tools provide helpful insights into which content types are accessed most often by visitors and help inform strategies for future updates and development phases.
Finally, website developers also have to consider performance optimization at this stage, ensuring that loading times are low and ensuring there is enough room on servers to handle larger amounts of incoming traffic in cases where there’s an expected spike in visits due to media coverage or other promotional activities.
8. Website Testing Phase
A Website Testing Phase is an essential component of the website development process. It evaluates whether the website’s features and functions have been correctly implemented and detects any potential bugs or errors in the code.

What is a Website Testing Phase?
This phase typically involves a combination of manual testing, automated testing, and user feedback gathering.
Manual testing involves a series of steps to manually check the functionality and performance of various parts of the site. During this phase, testers thoroughly examine each page to ensure that all aspects are working properly, with consideration for compatibility on different platforms.
Automated testing ensures consistency by repeatedly running tests with predefined components and parameters for analysis. On top of providing consistency in results across multiple iterations, automated tests can scale up when necessary to accommodate larger test scenarios.
User feedback is also highly valuable during this phase as it allows testers to understand how real users experience the site from functional and usability perspectives.
Tests such as A/B testing offer insights into which design elements users favor more and help shape future interface designs. Ultimately both manual and automated tests should be conducted comprehensively before launch to guarantee smooth user experiences on desktop or mobile devices.
9. Website Delivery and Launch
What is Website Delivery and Launch?
What is Website Delivery and Launch?
Website Delivery and Launch is the process of transferring a website from a development or staging server to an active production server and making it available to the public. The process ensures that all aspects of the website have been tested, implemented correctly, and securely migrated for optimal performance in its new environment.
The success of the deliverability and launch of a website depends on detailed planning and sound execution, such as:
- Identifying and addressing any potential technical difficulties during migration.
- Strengthening web security settings in line with best practices
- Optimizing code and content ahead of launch
- Creating URL redirects as necessary
- Validating functionality across devices
- Setting up analytics tracking mechanisms
- customApproving internal review cycles, such as QA testing prior to go-live
- Configuring scheduling options when appropriate for maintenance windows
- Submitting sitemaps for indexing by search engines for optimal SEO visibility post-launch
- And much more depending on scenarios unique to each site build
Once ready for release to the public domain, a measured approach is advised.
No matter how carefully managed, outages can occur so having plans set up in advance is highly recommended.
Consider parallel hosting solutions whereby an existing operational version sits in tandem with staged sites until stakeholders approve. Then switch over seamlessly by updating DNS settings based on a predetermined schedule.
10. Website Maintenance Phase
The website maintenance phase is critical when changes and updates are made to an existing website to keep it functioning correctly and appearing current.
What is the Website Maintenance Phase?
During this phase, modifications are introduced to improve visibility, usability, search engine ranking, performance, or overall user experience.
Content is updated or modified regularly to ensure the site’s information remains relevant and accurate.
Updates may include additions such as photos, videos, new blog content, and necessary bug fixes. Additionally, security measures will be implemented to stop attempts at malicious attacks.
Website maintenance may also involve working with a web host pertaining to storage space needed for data backups, possible hosting service upgrades, or increased bandwidth if page views increase significantly.
Numerous tasks are required, ranging from updating plug-ins used in the website’s back end to redirecting pages using 301 status codes so that users will be directed where they need to go quickly and efficiently. Relevant keywords must also continue to be added throughout various areas of the site’s structure for search engine indexing algorithms to locate them more easily when searching for related topics that correspond with customers’ queries.
A poorly maintained website can negatively affect its sales potential by not retaining clients due to lapsed communication and potentially egregious security issues arising if regular checks are not conducted. The website maintenance phase is, therefore, a vital stage during any website’s development process, which should never be neglected.
Conclusion Web Design Stages
What are the Stages of a Custom Web Design?
The stages of web design involve the conception, prototyping, design, development, testing, and launching of a website. A well-planned process will ensure a successful end result that meets the project’s business goals.
Conception is the first stage, where initial requirements for the project are established and objectives outlined. This helps to understand what needs to be created and how best to realize it.
Prototyping is then used to create the wireframe structure that serves as a blueprint for the visual aspect of the website. It determines how information should be displayed on page layouts, navigation menus, and links between pages.
Design is when aspects like colors, fonts, and imagery are added to give life to the website’s layout. The intent here is to keep brand identity in mind while being mindful of user experience across multiple devices, including desktops, tablets, and phones.
The development team follows where code is implemented according to agreed design plans. Programming languages used by developers include HTML, CSS, JavaScript, etc.
CSS frameworks like Bootstrap can also be used in web development cycles resulting in faster build times for websites or apps.
Testing then follows to check for bugs or usability issues with different browsers or devices before release. For example, cross-browser compatibility testing ensures all website elements display correctly across different browsers.
Finally, launching requires deploying your website or application online so users can access your content from anywhere, provided they have an internet connection; it’s likewise important to take measures to secure your site against potential hazards such as malicious attacks from hackers or DDOS bots.

